Table of Contents
Fuse replacement peculiarities
- Installing a new fuse, use only a one that of a similar type and with the same amperage. To clarify, if its rated current is higher than you need, it will fail to work out in emergency situations. However, underestimation of rated current is also not recommended. In this case, a fuse may blow and de-energize a circuit when you put a load even if there is no emergency.
- When replacing, you need to verify a current rate not only by checking both: label on a fuse body and marking of its socket.
- If a fuse blows again soon after its replacement, do not increase its amperage. Instead, you need to contact an expert to find out the issue.
- Always disconnect the battery before servicing high current fuses.
- Note! Never install a direct conductor instead of a fuse. So, in case you do not have a fuse that matches, you may temporarily use a good one of the same rating from the secondary circuit.
How to replace a blown fuse
- Turn your car off and remove the ignition key.
- Find your car fuse layout. Then, use it to identify the fuse responsible for the faulty device and find the box location. In addition, check its continuity visually or using special testers.
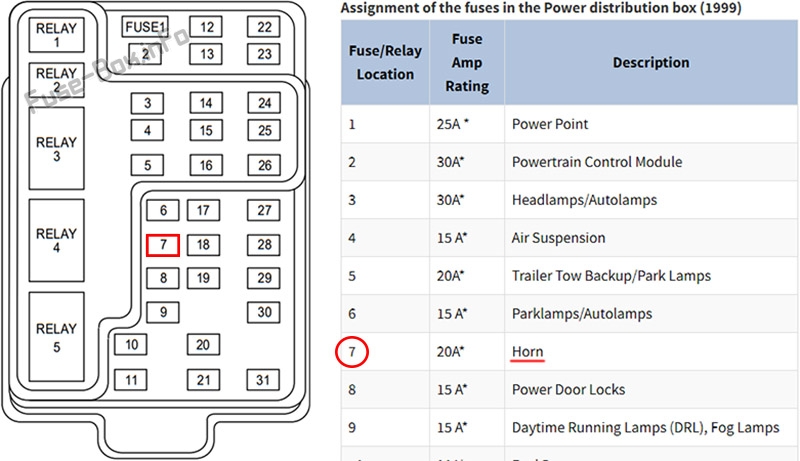
- Find the proper fuse box. Then, open it and remove the blown fuse. Usually, there is a special key or small plastic tweezers (fuse puller) inside the unit. Be sure you remember the slot you pluck it from.

- Insert a new fuse similar to the blown one. Be sure you insert it in the proper slot.
- Install the box protective cover back. Avoid water, dirt, and garbage getting inside the box as they may cause a short circuit or corrosion. In other words, they may damage your car.
- Check the device is operating well. If it does not work or the fuse has blown again, you need to contact a specialist.



